Our Strength Lies On
We have a well-managed factory unit that equips all the required modernized facilities for production of a qualitative range of innovative products.
PTFE piston rings have been manufactured and used in oil-free compressors for many years. The demand for seals suitable for oil-free applications has grown considerably in recent years. This development has largely been driven by increased aware- ness of environmental concerns, more stringent regulations and the constant need to achieve further cost reductions.
Meanwhile, our solutions have established themselves as essential elements in numerous industrial, engineering and consumer goods sectors like:
Properties of PTFE can be improved by adding additives as carbon, graphite, glass etc.
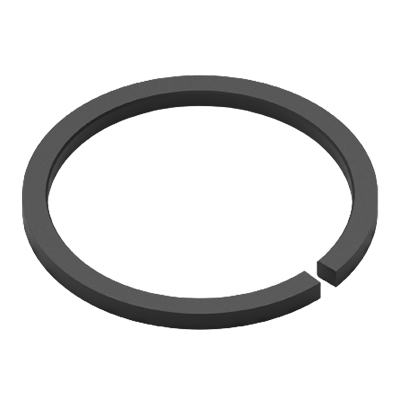
Piston rings with straight joints are used for sealing pressure differences above 15 bar. With this gap, leakage is slightly higher than with piston rings that have a scarf joint. Due to the high compressor speeds (rpm) typically achieved today, the loss of gas from leakage has a minor impact on Compressor performance. The amount of gas leakage is negligible.

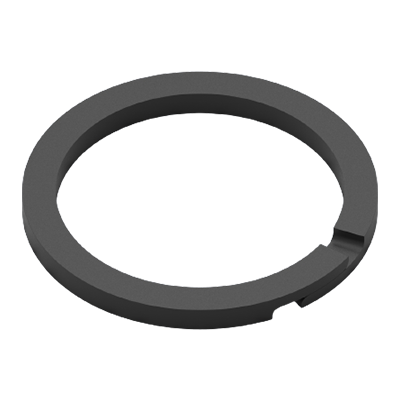
Piston rings with scarf joints are used for sealing pressure differences above 15 bar. During the run-in period the sealing effect (tightness) of scarf joints is slightly better than that of piston rings with a straight joint.
The overlapped joint achieves a favourable sealing effect. For this reason, it is primarily used for sealing gases with a specific light weight. Due to the occurrence of bending stress and the resulting risk of breakage in the overlapping areas, piston rings with overlapped joints should only be used in compressors operating with pressure differences of a maximum of 15 bar.

Our gas-tight piston rings achieve the best sealing effect. The special design of the joint reduces leakage to a minimum. As with the overlapping joint the level of differential pressure is limited to a maximum of 15 bar. With regard to assembly please note that the piston ring achieves its good sealing effect only in one direction of pressure.
Guide rings and bands serve to prevent any contact of the piston and/or rod with the cylinder wall in order to avoid subsequent damage to these parts. Usually, guides with straight or scarf joints are used. The scarf joint is the most commonly used joint.

Straight Joint
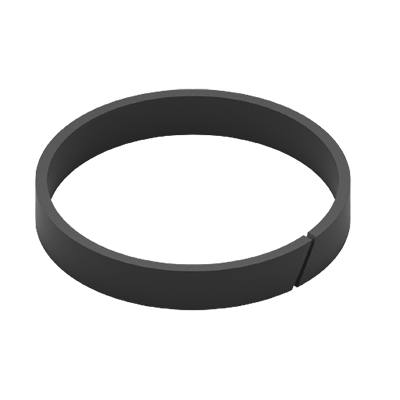

Scarf Joint

Continuous
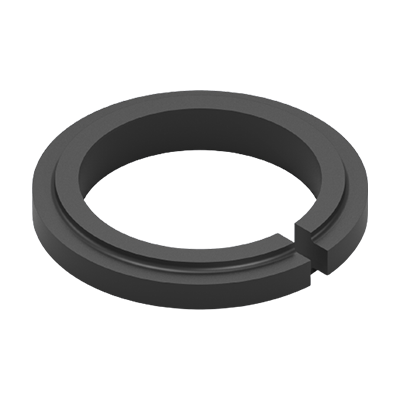

Shouldered with straight Joint
Guide rings with scarf joints provide the advantage of fully running across the cylinder contact surface, thus causing no “markings” on the surface unlike the straight joint.
Guide rings with straight or scarf joints can only be fitted if no more than 1/3 of the guide ring width overruns the valve nests inside the cylinder. If several valve nests are overrun, one-piece shrink fitted guide rings are used. Depending on the respective application, piston guide rings with axial and/or radial balancing grooves may be used as well. The dimensions of the guide ring depend on the particular application
We have a well-managed factory unit that equips all the required modernized facilities for production of a qualitative range of innovative products.

To completely satisfy a customer, we mainly focus on the quality level of our in-use working methodology used for developing these offered products.

Our sophisticated infrastructure set-up which is outfitted with modern machines and equipment aids the employees in the smooth execution of the operations.
Fill in your details and
our team will share complete information with you.
